Abstract
Chronic graft-versus-host-disease (cGVHD) remains a common and poorly understood cause of late non-relapse morbidity and mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT). T cells and IgG-producing B cells mediate cGVHD development and perpetuation, but molecular mechanisms driving immune pathology require further study. We have shown that B cells from cGVHD patients are B Cell Receptor (BCR)-activated and primed for survival. In a mouse model of bone-marrow transplantation (BMT) with cGVHD manifestations, BCR signaling is promoted by alloantigens and BAFF (Jia et al., Blood 2021). BCR signaling is a viable therapeutic target in cGVHD, but other targetable pathways that promote pathological BCR-activated B cells remain largely unknown.
Our single cell RNA-sequencing study of B cells from the peripheral blood (PB) of HCT patients identified 'Absent in Melanoma 2' (AIM2) as a prime candidate for further study (ASH abstract 2019, Poe et al., manuscript submitted). AIM2 was a signature gene in a BCR-activated subset after HCT, and AIM2 transcripts were significantly increased in a pre-germinal center (GC) B cell subset in cGVHD vs. no cGVHD patients (adjusted p=0.049). AIM2 incites inflammasome-mediated pyroptotic cell death in myeloid cells, but the function of AIM2 in B cells is largely unknown. AIM2 is expressed by CD27+ antigen (Ag)-experienced B cells in healthy individuals (HI) (Svensson et al., PlosOne 2017) and emerging evidence suggests that AIM2 promotes antibody production (Yang et al., Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021). We hypothesize that AIM2 promotes pathological BCR-activated B cells and anti-host IgG production in cGVHD.
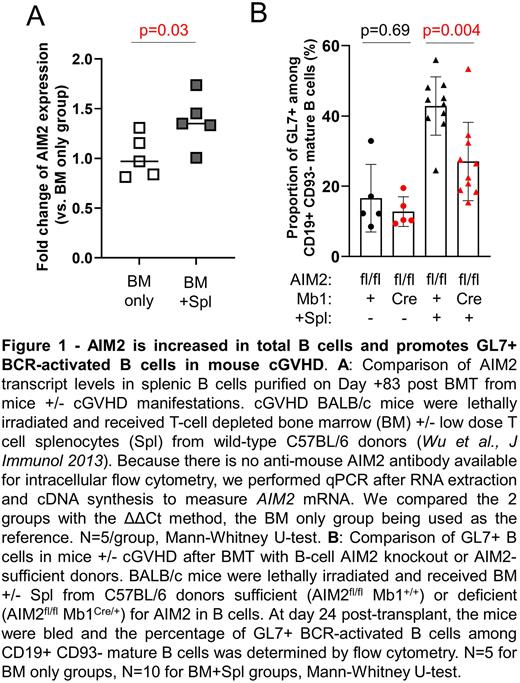
Using intracellular flow cytometry (IFC) and PB samples from HI (n=27), we first confirmed that the AIM2 protein is mainly expressed by CD27+ Ag-experienced B cells. Specifically, 88% and 99% of the IgD+ pre- and IgD- post-GC CD27+ B cells expressed AIM2, respectively. In HCT, we found a significantly higher proportion of AIM2+ cells in the circulating CD27+ IgD- post-GC B cells from cGVHD patients (n=7) vs. no cGVHD patients (n=5) (p=0.02). We also found significant overexpression of AIM2 transcripts in B cells from mice with cGVHD manifestations vs. no cGVHD mice (n=5/group, p=0.03, Figure 1A). To determine if Ag-activation together with other extrinsic factors typically encountered by B cells after HCT induced AIM2 expression by purified CD27- B cells from HI, we used IFC. The proportion of AIM2+ CD27- B cells increased after BCR +/- Toll-like receptor 7 or 9 stimulation only when IFNγ was present.
Next, we studied the function of AIM2 in B cells. Unlike myeloid cells, CD27+ B cells from HI did not undergo pyroptotic cell death after stimulation with double stranded DNA. This lack of pyroptosis was not due to a deficiency in the inflammasome components and B cells had the capacity to undergo pyroptosis after exposure to the NLRP1/3 activator, nigericin. To assess effects of AIM2 on specific IgG production, we used AIM2 KO mice in a hapten-carrier immunization model (NP-KLH + alum i.p.). AIM2-KO mice had larger splenic GC vs. WT controls at day 8 post-immunization (p<0.0001). GC enlargement paradoxically associated with lower anti-NP IgG levels (p=0.03). Finally, having previously shown that BM+Spl recipients have a significantly higher proportion of GL7+ BCR-activated blood B cells (Jia et al., Blood 2021), we asked whether AIM2 promoted GL7+ B cells in cGVHD. To address this, we used AIM2-floxed mice, kindly supplied by Genentech, to breed AIM2fl/fl Mb1Cre/+ conditional KO mice (AIM2-CKO), deficient in AIM2 only in B cells. We then used these AIM2-CKO vs. AIM2fl/fl Mb1+/+ control littermates mice which are AIM2-sufficient as BMT donors. At day 24 post-BMT, recipients of BM+Spl from AIM2-CKO mice had a significantly lower percentage of mature (CD19+ CD93-) GL7+ B cells in PB vs. recipients of BM+Spl from the AIM2-sufficient littermates (n=10/group, p=0.004, Figure 1B). This was not due to baseline B cell differences in donor CKO mice. These results are being confirmed at later time points in ongoing, additional experiments. Our data show that AIM2 promotes IgG-producing B cells and circulating GL7+ B cells, suggesting that AIM2 plays a novel inflammasome-independent role in cGVHD B cell pathology. We are actively investigating how AIM2 effects alloantibody production and cGVHD development, so that therapeutic targets can be identified.
Disclosures
Ho:Allovir: Consultancy; Alexion: Consultancy; Jazz: Research Funding; Omeros: Consultancy. Sarantopoulos:Rigel Pharmaceuticals: Other: receives supplies for clinical trials.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.